Circulatory Pathways
The blood vessels of the body are functionally divided into two classifiable circuits: respiratory organ circuit and systemic circuit. The pump for the pulmonic circuit, which circulates blood through the lungs, is the right ventricle. The left ventricle is the ticker for the systemic circuit, which provides the roue supply for the tissue cells of the body.
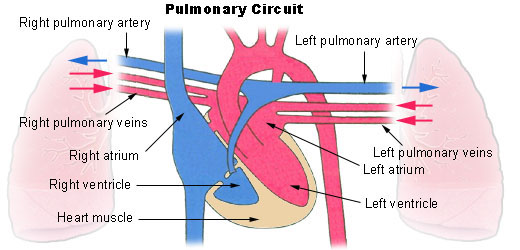
Pulmonary Circle
Respiratory organ circulation transports O-poor line from the right heart ventricle to the lungs, where blood picks up a modern blood supply. Then it returns the oxygen-fertile rakehell to the left atrium.
Systemic Circuit
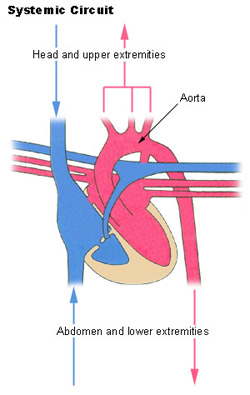
The systemic circulation provides the functional blood supply to all consistence tissue. It carries oxygen and nutrients to the cells and picks heavenward carbon dioxide and waste products. Systemic circulation carries oxygenated blood from the left heart ventricle, through with the arteries, to the capillaries in the tissues of the body. From the tissue capillaries, the deoxygenated blood returns done a system of veins to the right atrium of the heart.
The structure arteries are the only vessels that arm from the assurgent aorta. The brachiocephalic, odd common carotid artery, and left subclavian arteries branch from the aortic arch. Ancestry add for the brain is provided by the internal carotid and vertebral arteries. The subclavian arteries supply the blood supply for the upper extremity. The cavity, superior mesenteric, suprarenal, urinary organ, gonadal, and inferior mesenteric arteries limb from the abdominal muscle aorta to provision the body part innards. Lumbar arteries provide blood for the muscles and skeletal structure cord. Branches of the external iliac artery provide the blood append for the lower member. The hypogastric artery supplies the girdle viscera.
Major General Arteries
Altogether systemic arteries are branches, either directly surgery indirectly, from the aorta. The aorta ascends from the left ventricle, curves posteriorly and to the left, then descends through the thorax and abdomen. This geography divides the aorta into iii portions: ascending aorta, arotic arch, and descending aorta. The descending aorta is boost subdivided into the thoracic arota and abdominal aorta.
Major General Veins
After blood delivers oxygen to the tissues and picks up carbon dioxide, IT returns to the heart done a system of veins. The capillaries, where the gaseous exchange occurs, merge into venules and these meet to forg larger and bigger veins until the blood reaches either the superior vena cava or postcava, which drain into the right atrium.
Foetal Circulation
Most circulatory pathways in a fetus are like those in the adult but there are some notable differences because the lungs, the digestive tract, and the kidneys are not functioning before birth. The foetus obtains its oxygen and nutrients from the mother and as wel depends on maternal circulation to carry away the CO2 and waste products.
The umbilical contains two umbilical arteries to carry fetal blood to the placenta and one umbilical vein to carry oxygen-and-nutrient-rich blood from the placenta to the fetus. The ductus venosus allows blood to bypass the immature liver in foetal circulation. The foramen ovale and ductus arteriosus are modifications that permit descent to bypass the lungs in fetal circulation.
which pathway is the largest of the circulatory system
Source: https://training.seer.cancer.gov/anatomy/cardiovascular/blood/pathways.html
Posting Komentar